Published On Mar 17, 2024
On March 14, SpaceX's Starship embarked on its third test flight from the Starbase facility in South Texas, marking another significant milestone in the development of what is currently the largest rocket ever built. This flight was particularly noteworthy for its demonstration of orbital velocity achievement and other key capabilities that are crucial for future lunar missions, especially within the framework of NASA's Artemis program which aims to return humans to the Moon and beyond.
One of the highlights of this test flight was the propellant-transfer demonstration, an essential capability for sustaining longer missions in space by allowing spacecraft to refuel while in orbit. This technology is of particular interest to NASA as it aligns with the goals of the Artemis program by potentially extending the reach and duration of human exploration missions. The success of such a demonstration could pave the way for more ambitious missions, including those targeting the Moon, Mars, and possibly other destinations in the solar system.
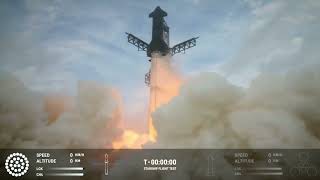
Before the launch, the teams conducted thorough final checks on weather conditions at T-60 minutes, ensuring that all parameters were within acceptable limits for a safe launch. Given the favorable conditions, the launch director proceeded with the propellant loading process, filling the Starship and its Super Heavy booster with liquid methane and liquid oxygen. This process, completed by T-45 minutes, is critical, not only because of the technical requirements but also due to the sheer volume of propellant involved. The Super Heavy's 33 Raptor engines, upon ignition, consumed around 40,000 pounds of propellant per second.
At T+2 minutes and 44 seconds, the stage separation occurred. This was executed flawlessly, with most of the booster engines shutting down except for three, allowing for a controlled separation. Immediately after, the upper stage's six engines ignited, marking the start of its journey to orbit.
During its ascent, the booster initiated a boost-back burn, reorienting itself for a return to Earth. This maneuver was captured in incredible detail by the onboard cameras, showcasing the booster’s-controlled descent and re-entry preparations.
As the booster approached the Gulf of Mexico, it performed a landing burn, aiming for a soft splashdown. Although the feed was lost shortly before landing, this maneuver is critical for SpaceX's vision of reusable rockets.
The launch generated significant attention not only for its visual spectacle with the water suppression system at the launch pad mitigating the intense heat and force from the rocket engines, but also for the critical technologies being tested. Among these, the in-space propellant transfer is perhaps the most groundbreaking. This operation involved transferring fuel from one of Starship's tanks to another in orbit, a process complicated by the cryogenic nature of the fuel which needs to be super-cooled to remain liquid. The stability of Starship during this operation is paramount, as any adverse effects could jeopardize the mission's success.
Keywords:-
SpaceX starship plan, Starship next launch, SpaceX and NASA, SpaceX starship launch, SpaceX vs NASA, starship booster explosion, Why did the Starship explode, Why did the Starship blow up, starship launch, Spacex Starship launch,Spacex super heavy launch,spacex super heavyrocket,SpaceX and Musk, musk leaves spacex, FAA vs SpaceX over starship